For broadcasters navigating the intricate landscape of live streaming, understanding and managing Understanding and managing latency is pivotal for broadcasters navigating the intricate landscape of live streaming. In a realm where every second counts and viewers’ expectations for seamless experiences are higher than ever, latency can be the make-or-break factor in your broadcast’s success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’re unpacking everything you need to know about latency in live streaming, from the basics of latency and why it’s essential to the fastest low-latency streaming protocols available.
Understanding and optimizing latency is essential for content creators and broadcasters to ensure that your audience is immersed and as close to “in the moment” as technically possible.
What is low-latency streaming?
At its core, latency is a measure of time. It’s the time taken for data to travel from point A to point B. In the context of video streaming, it refers to the delay between actions happening in the physical world — such as a football being kicked — and those actions being displayed on your screen.
It’s an inherent part of any live streaming setup, but the extent of latency can vary widely depending on the technology and configuration. There are typically two categories for low latency, and either one can be used depending on the use case.
The first category is low latency, which is a delay of several seconds and is acceptable for most live broadcasts where there is no two-way interaction. The second category is ultra-low latency, which refers to a delay of less than a second and is crucial for interactive streaming.
To get an idea of scale, consider this: traditional broadcast television typically has a 5- to 7-second lag. Today, we measure high-performance streams in single-digit seconds, sometimes fractions of a second.
Types of streaming latency
For broadcasters, understanding the different types of latency is critical in diagnosing the lag and strategizing how to minimize it effectively. Here are the most common types of latency in streaming:
- Glass-to-glass latency: The entire delay from the capture phase through encoding, transmission, decoding, and rendering of the video on screen
- Encoding latency: The time it takes to process the raw video and audio data into a format that can be streamed over the internet
- Network latency: influenced by the distance between the streaming server and the viewer’s device; The longer this distance, the more hops the data has to make, increasing the delay
- Playback latency: The result of buffering and the capabilities of the viewer’s device
Why does streaming latency matter?
Latency directly influences the viewer’s experience. High latency can lead to spoilers via social media or other channels before the streamed content catches up, diminishing the live aspect of the stream. For interactive streams, such as live Q&As, gaming, or auctions, high latency can disrupt the flow, making real-time engagement problematic.
In a world where live interactions are becoming increasingly primary and expected by viewers, any delay is detrimental to the experience.
For live sports, the stakes are sky-high. Immersive sports experiences need to keep pace with stadium cheers and tackles, requiring lightning-quick streams. iGaming demands even more, with ultra-low latency streaming being the difference between a winning move and a missed betting opportunity.
Low latency is significant in live streaming for a multitude of use cases. From live auctions, where every millisecond counts, to real-time video discussions that rely on immediate feedback, low latency has evolved from a “nice to have” to an essential feature.
What causes video streaming latency?
You’ve likely heard the adage that a chain is only as strong as its weakest link. This is especially true when it comes to video streaming latency.
Video streaming latency is introduced at various points throughout the streaming workflow. It can be caused by your choice of content delivery network (CDN), encoder settings, protocols, and network conditions.
How to reduce video streaming latency
Reducing latency is critical for real-time and interactive content. Thankfully, several strategies and technologies can help trim the lag and bring your live video streaming closer to the real-time experience. Here’s what you can do.
1. Use a global CDN
Choosing a CDN with a wide geographical spread can significantly decrease the distance between the server and the end-user. By strategically placing servers near your entire audience, you can minimize transmission delays and achieve lower latency.
2. Optimize your encoder settings
How you configure your encoder settings can also reduce your latency. Choosing the correct codec and reducing the bitrate without compromising video quality can lead to faster processing and delivery times.
3. Leverage protocols designed for low latency
Certain protocols are designed to facilitate low-latency streaming, minimizing delays inherent in traditional streaming methods. Additionally, some protocols even facilitate direct ultra-low-latency streaming. We will cover the recommended protocols in-depth later in this guide.
4. Conduct regular network assessments
Assessing your network conditions to identify and rectify bottlenecks helps maintain optimal streaming performance. It’s critical to test your stream on as many devices and operating systems as possible before the event to identify any potential playback issues.
By implementing these techniques, broadcasters can achieve lower latency, providing viewers with a more immediate and engaging live streaming experience.
When to use low-latency streaming
Depending on the content and context, different use cases will require different latencies to achieve the best balance between real-time interaction and stream quality.
Here’s a look at six streaming use cases and how latency impacts each one.
1. Live sports broadcasting
For live sports events, low-latency streaming is significant. A recent survey reveals that the average sports latency is currently 9 seconds, with a target of 5 seconds within three years, aiming to match broadcast latency.
Fans expect to see plays unfold in close to real-time, without spoilers from social media or text messages ruining the suspense. A delay of even a few additional seconds can significantly impact the viewer’s experience.
That’s why low-latency streaming solutions are often employed in this context to ensure that the action is delivered as it happens, keeping viewers engaged and immersed in the game.
Real-time latency is also valuable in sports broadcasting scenarios where in-game and microbetting are involved. The ideal latency for these use cases is typically 1 to 2 seconds, to align video with data latency. Horse racing often goes at an even lower latency of around 500ms.
2. Online casinos
In the realm of live casinos and iGaming, latency is a critical factor for both players and spectators.
For players, high latency can hinder gameplay, affecting reaction times and competitiveness. For spectators, ultra-low latency is crucial to keep the stream as close to live as possible, enabling viewers to react and interact with the content in near real-time.
This is especially important for interactive elements such as live chats or polls, where immediate feedback enhances the communal viewing experience.
3. Corporate webinars and conferences
Corporate webinars and virtual conferences have different latency requirements. Here, a slight delay is often acceptable if the focus is on delivering content clearly and uninterrupted, rather than facilitating instant interaction.
Standard latency streams are typically used, balancing quality and real-time engagement without the need for the immediacy found in sports or gaming. This enables higher-quality video and audio, ensuring that presentations are professional and impactful.
It’s worth noting that webinars with more interactive elements, such as Q&As or breakout rooms, do benefit from real-time latency since they require person-to-person communication. However, this is not a requirement for every stream of this nature.
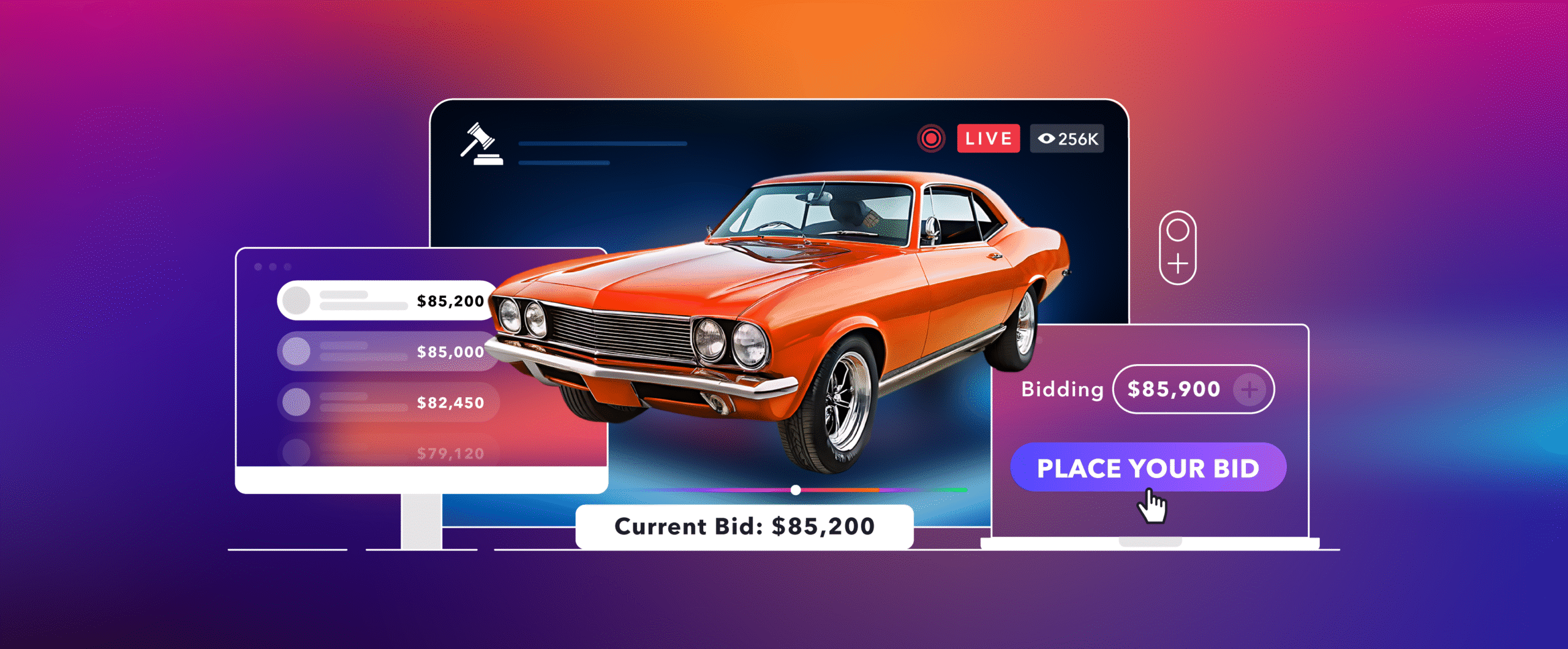
4. Live auctions
Live auctions are a unique use case where ultra-low latency streaming is crucial. Bidders need to see and react to the auction in real-time to place their bids effectively.
Any significant delay can result in lost opportunities or confusion among participants. Therefore, platforms hosting live auctions prioritize minimizing latency to facilitate a fair and dynamic bidding environment, mirroring the experience of being physically present at an auction.
5. Live shopping
Live shopping is an online sales event that involves selling products in live streams. A salesperson showcases products to appeal to shoppers, demonstrating the practical uses of household products or styling clothing items.
Oftentimes, products are offered at special pricing that expires at the end of the stream. The idea is to create a sense of urgency and encourage people to make impulsive purchases.
Although some latency is acceptable with live shopping, low latency can be valuable for facilitating interactions among shoppers in the chat. This helps to build a community around the brand.
6. Remote production (REMI)
Remote production (REMI) is another common use case for low-latency streaming. REMI involves recording a stream in one location but handling production in another. The idea is to save money on costs typically associated with on-site production.
This technique is valuable in live event production for broadcasts, sports, and concerts, which involve varying amounts of latency. However, latency is significant for REMI because the stream needs to be transported from the source to the producers in as little time as possible to ensure smooth production.
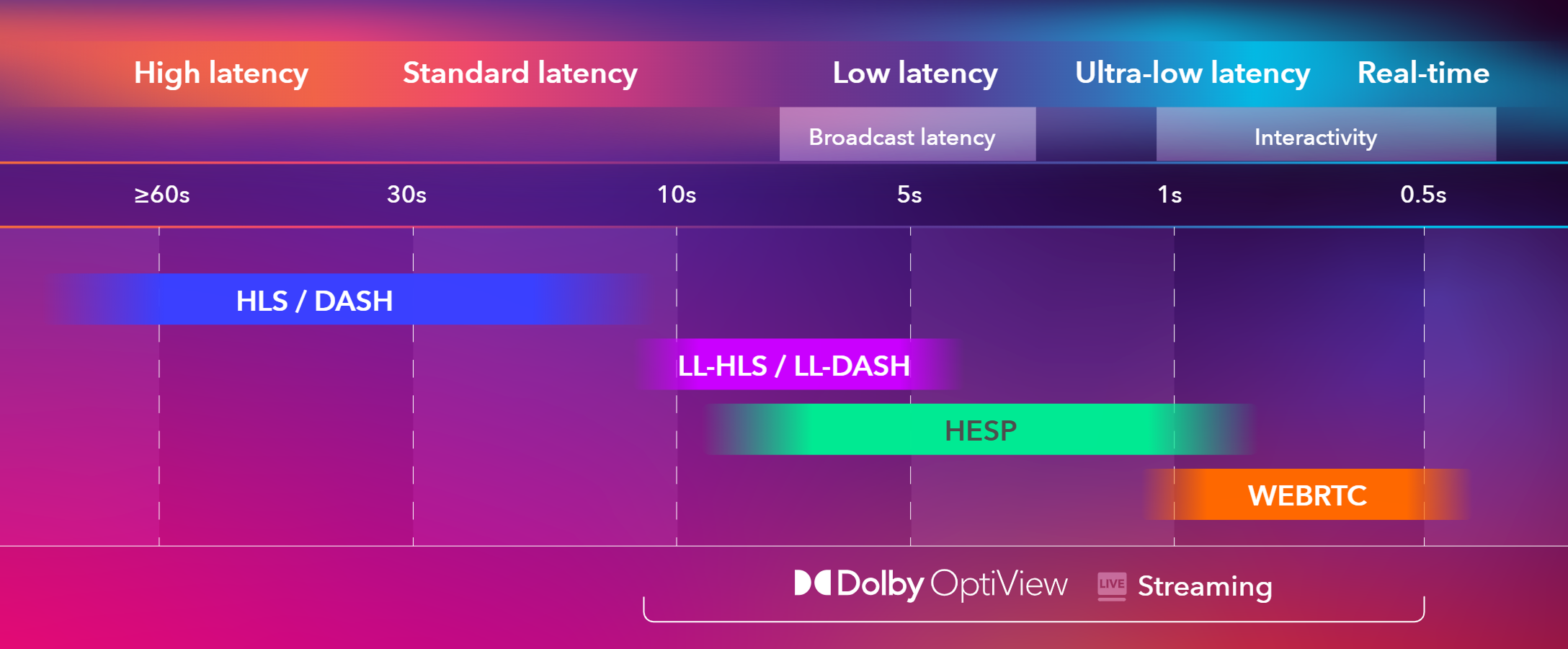
Protocols used for low-latency streaming
Several protocols are used for low-latency streaming, including WebRTC, HESP, LL-HLS, and LL-DASH. Let’s take a close look at each of these streaming protocols.
WebRTC
WebRTC is used for real-time streaming in scenarios where latency needs to be under half a second. Originally developed to bring the power of real-time communication to the browser – without the need for plugins like Flash – It uses a peer-to-peer architecture that has since been widely adopted across platforms, including mobile devices, smart TVs and set-top boxes. However, some limitations still remain depending on the platform.
Its low-latency streaming, combined with its HTML5 native approach, makes it a top contender in today’s streaming environment.
Low-Latency HLS and DASH
Low-latency HLS (LL-HLS) and LL-DASH are the low-latency variants of HTTP-based streaming protocols, namely HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH). They scale over standard CDNs, offer adaptive bitrate (ABR) capabilities, and achieve latency ranges of 3-7 seconds.
While HLS and DASH are popular choices for both high- and low-latency streaming, they fall short in delivering ultra-low-latency experiences.
HESP
High-Efficiency Streaming Protocol (HESP) is another great HTTP-based protocol for low-latency streaming.
HESP has several advantages over LL-HLS and LL-DASH, as it can further reduce latency to about 1 second and bring fast channel change times. Its full adaptive bitrate (ABR) capabilities ensure low latency even under unfavorable network conditions.
The future of low latency in live streaming
The future of low-latency streaming is poised for significant advancements, driven by emerging technologies and growing demand for real-time interactions.
As the world becomes increasingly connected, the expectation for instant access to live content is becoming the norm, pushing the boundaries of current streaming capabilities. Innovations in 5G technology, edge computing, new streaming protocols, and more efficient video compression algorithms are at the forefront of this evolution.
These technologies promise to reduce latency, making near-instantaneous streaming a reality. This will not only enhance experiences in entertainment and iGaming but also unlock new possibilities in remote education, telemedicine, and live event coverage, where immediacy is crucial.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into streaming networks will play a pivotal role in optimizing the delivery of live video content.
By predicting bandwidth fluctuations and viewer preferences, AI can dynamically adjust stream quality, ensuring smooth playback without buffering, even in ultra-low latency streaming scenarios.
Final Thoughts
With the knowledge and strategies outlined in this guide, content creators and broadcasters are better equipped to tackle latency head-on, delivering seamless live experiences that captivate and engage audiences worldwide.
By understanding the nuances of video latency and applying best practices to mitigate its impact, the streaming world can continue to deliver immersive, real-time experiences that draw viewers closer than ever to the heart of the action.
Looking for an end-to-end solution to help you achieve low latency in your streams? A powerful streaming solution like Dolby OptiView is an excellent choice. Contact us today to discover how we can assist with your low-latency streaming initiatives.
Low-latency streaming FAQs
There is no one-size-fits-all answer – the best low-latency protocol depends on your specific use case and requirements. There are several protocols for low-latency streaming, including WebRTC, HESP, LL-HLS, and LL-DASH. Each streaming protocol offers distinct characteristics, including latency, scalability, and device support.
Low-latency streaming is utilized in cases where real-time interaction is required or to bring viewers closer to the action. Use cases include live sports streaming, live casino, online auctions, sports betting, webinars, live shopping, remote production, and more.
Low-latency streaming brings various benefits. For live sports, for example, it’s the basis for interactive use cases such as social engagement and in-game betting. Low latency also avoids spoilers from social media. For use cases like live casino, it maximizes the number of hands played, while for auctions, it maximizes the number of bids.